Tumor Growth: What Causes It and How Medications Help
When cells in your body start multiplying out of control, they can form a mass called a tumor growth, an abnormal collection of cells that may be benign or cancerous. Also known as neoplasia, tumor growth isn’t just about size—it’s about behavior. Some tumors stay put; others spread fast, damaging nearby tissue and organs. What triggers this? It’s often a mix of genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors like smoking, UV exposure, or chronic inflammation.
Not all tumor growth leads to cancer, but when it does, treatment becomes urgent. Drugs like chemotherapy, medications designed to kill rapidly dividing cells are common. Capecitabine, for example, is an oral chemo drug used for breast and colorectal cancers—it gets converted into a toxin inside tumor cells, stopping them from multiplying. Then there are tumor suppression, the body’s natural defense system that halts abnormal cell division, which can be weakened by mutations in genes like p53. When that happens, treatments aim to restore or replace that lost control. Some drugs target specific markers on tumors, like hormone receptors or proteins, to block signals that fuel growth.
Side effects matter, too. Chemotherapy doesn’t just hit cancer cells—it affects fast-growing healthy cells, like those in your hair, gut, and bone marrow. That’s why patients often feel tired, lose appetite, or get infections more easily. Newer treatments try to be smarter, using targeted therapies or immunotherapies to focus only on tumor cells. But even then, monitoring is key. Doctors track tumor markers in blood tests, scan for shrinkage, and watch for signs of resistance. It’s not just about killing cells—it’s about managing the whole picture.
You’ll find real-world guides here on how specific drugs like capecitabine, ampicillin, or even pain relievers play a role in managing symptoms or side effects tied to tumor growth. Some posts cover how to handle nausea from chemo, others explain why certain antibiotics are used in immunocompromised patients with tumors. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer, but understanding the basics helps you ask better questions and make smarter choices with your care team.
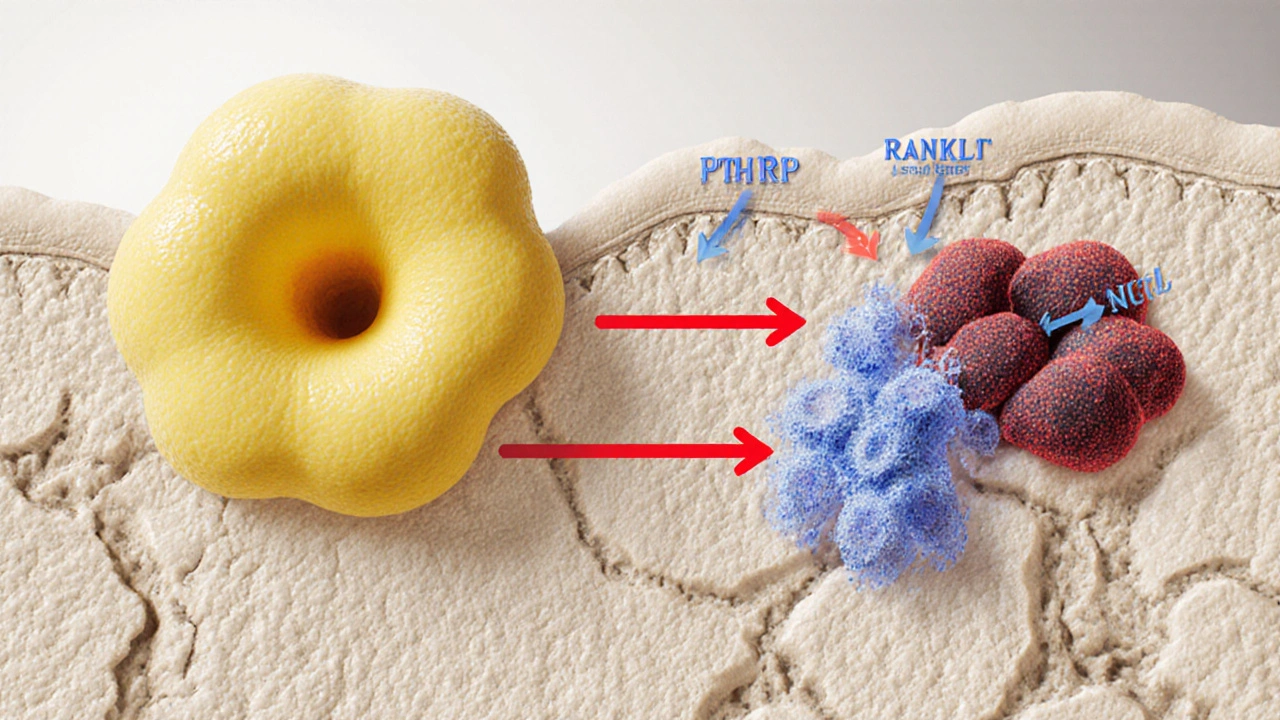
Learn how tumor growth harms bone health, the mechanisms behind bone metastasis, signs to watch for, and strategies to protect skeletal strength.